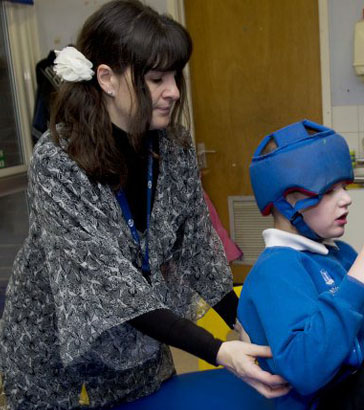
Among other responsibilities, a Special Educational Needs Coordinator (SENCO)
ensures that parents and carers liaise with each other, makes sure that individual education plans are in place and advises
other staff about the school policy for children with SEN.
The SENCO's role is also management-orientated. In many cases this
will mean you will first need to be on the senior leadership team before you can become a SENCO.
Find out more about becoming a SENCO here.

Engaging parents is not always an easy task. This article describes how family partnership training can enable staff to
build and maintain purposeful relationships with parents.
Critically reflect on the SENCO's practice. Do they guide, direct and support new teachers? Do they consult, engage and communicate effectively with parents/carers and students to enhance the learning progress?

Communication is a vital skill that all children need to learn. Without it they will not reach their full potential. An
evaluation by a certified speech and language therapist can help determine if a child is having difficulties.
A speech and language therapist works closely with teachers and health professionals including doctors, nurses and psychologists.
This NHS page describes the role of a speech and language therapist, including information on entry requirements and training
programmes.
Speech and language therapists (2)
In the first audio clip a speech and language therapist, Charlotte Parkhouse, describes how she works with school staff.
-
 Working with school staff1:18
Working with school staff1:18 -
 Working in a special school2:44
Working in a special school2:44
In the second clip a speech and language therapist, Laura Stevenson, talks about the range of speech, language and communication difficulties found in a special school, her role and how she works with others to help pupils to work towards targets.
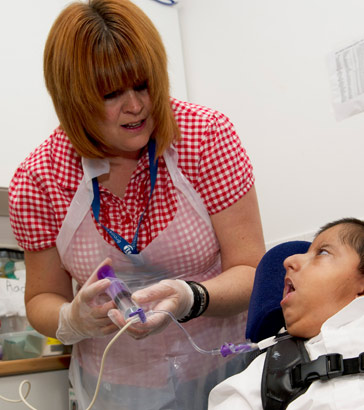
Physical health needs are common and require effective management and ongoing assessment and interventions to minimise
complications that can impact on learning. The range of physical health needs includes epilepsy, visual and hearing impairments,
mobility and balance issues, gastric reflux and swallowing and choking problems.
Critically reflect on the issues relating to risk assessment and management regarding the eating and drinking needs of the
children that you are involved with and how colleagues meet them safely.
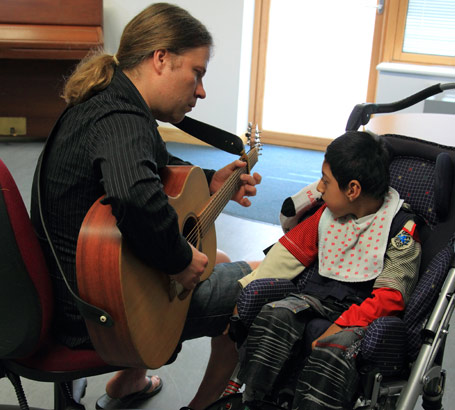

Music therapists use music creatively to address social, emotional or physical problems. They work with children and adults
of all ages and social backgrounds and in a variety of settings.
Read more about the role of the music therapist here.
Music therapists (2)
In these audio clips a music therapist explains the difference between music therapy and using music as part of lessons and explains the benefits to pupils of working in partnership with colleagues from other professional disciplines.
-
 Working with school staff1:16
Working with school staff1:16 -
 Working in a special school0:48
Working in a special school0:48
In the video a music therapist explains how music can help promote communication in a story led by a speech and language therapist.
Therapists at work
In the first video a speech and language therapist discusses feeding issues and their links to speech.
In the second video a physiotherapist gives her report at a review meeting.
-
 Speech and language therapist3:12
Speech and language therapist3:12 -
 Physiotherapist3:49
Physiotherapist3:49
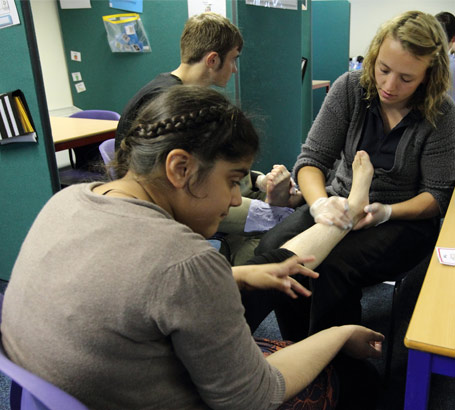
Identify all the visiting professionals involved with the children and families where you practice.
Critically review their contributions to meeting the health needs of children that supports their learning.
Critically appraise policies and protocols that are in place to enable the health needs of children and young people to be
met safely.

Occupational therapists are health and social care professionals who are specifically and uniquely trained to address the
relationship between occupation and physical and mental well-being. They help young people up to 18 years of age to access
education and engage in activities at home and in school.
Occupational therapists are one of the few professionals to work with children across all settings – in the home, at
school, and in the community – enabling children to develop their skills and increase their independence. Working with
children, occupational therapists set goals to enable them to participate in activities they need or want to do, to help children
get the most from life.
For more information on occupational therapists' work with children visit the site below.
of children

Identify two children that you have been involved with who have contrasting needs and write profiles of:
- The impact and implications on their families;
- How their needs are met;
- Who is involved in meeting them; and
- The resources that have been necessary to support their learning and wider inclusion.

Emerson E. and Baines S. (2011) Health inequalities and people with learning disabilities in the UK. Tizard Learning
Disability Review 16 (1) 42-48.
Liley A. and Manthorpe J. (2003) The impact of home enteral tube feeding in everyday life: A qualitative study. Journal
of Health & Social Care in the Community 11 (5) 415-422.

Royal College of Nursing (2011) Meeting the health needs of people with learning Disabilities. London: RCN.
