People who find it hard to move &endash; for example, those with multiple disabilities
&endash are most at risk of developing body shape distortions. This is because
they often sit and lie in limited positions. If we understand why certain
postures are distorting the body, we can correct them. Postural care is
about using the right equipment and positioning techniques to help protect
and restore body shape.
Postural Care Action Group, 2011
Therapeutic skill lies in recognition and correction of seemingly innocuous
deviations from symmetry before damage to skeletal structures occurs.
Goldsmith and Goldsmith, 2007

Postural care is about protecting someone's body
shape. Failure to protect body shape can have serious consequences for
a person's health and quality of life. It can even cause premature death.
Postural Care
Action Group, 2011
The development of a postural care service will
seek to allow individuals to enjoy life while providing them with supported
symmetrical postures in sitting and lying, with standing being included
if appropriate, over most of 24 hours a day to protect body structures.
Goldsmith and
Goldsmith, 2007
Postural care for an individual may include some of the following:
- Seating systems for functional sitting.
- Equipment for side-lying, prone and postural drainage.
- Moulded seating for wheelchairs.
- Pressure relief (eg foams, gels, and flotation cushions).
- Standing frames.
- Postural jackets, shoes, splints, etc.
- Sleep systems.
- Hydrotherapy.
- Mobility devices.
(This list is based on: Canterbury Christ Church University, 2009 and Goldsmith
and Goldsmith, 2007)
It is important to use and maintain equipment with regard to health and
safety, infection control and
manual handling.

http://www.mencap.org.uk/posturalcare

Some of the advantages of weight bearing in a standing frame are that it:
- Stimulates sensation in feet and legs.
- Helps prevent osteoporosis.
- Is good for breathing, circulation, and bladder and bowel function.
- Stretches the leg muscles.
- Positions the child or young person at the same height as others.
- Allows fine motor movements.
- Maximises the ability to stay upright when transferring from one piece of equipment to another.
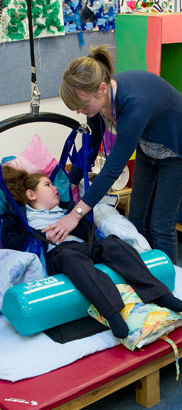
The professionals I've come across are very aware
of the need for good positioning, good postural care, but parents aren't.
And I think that professionals are afraid to tell parents what the future
may hold for their children... But that can be really detrimental for
the child... Most importantly, I didn't understand the importance of using
[a sleep system] and the consequences of not using it.
From 'Milly's story' (video)
There is not one child in the whole of the Wakefield
[District Children's Services] complex needs field that has a dislocated
hip and that's phenomenal.
From 'The Wakefield
story' (video)
Postural Care
Action Group, 2011b
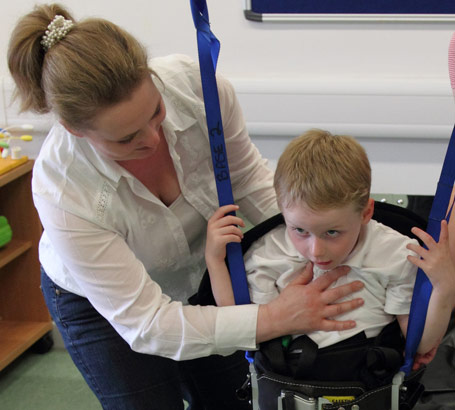
Formal structured training – generic and individual – for staff
and families is important in posture management. The success of postural
management can be compromised by trying too much too soon.
Positioning needs may vary with the presence of different complications
(eg breathing difficulties, epilepsy, reflux, etc.)

In school, body positioning can affect children and young people's ability
to communicate, socialise, anticipate, participate and, therefore, to learn.
Read the case study below describing how changes in body positioning improved
the quality of life of a four-year-old boy.

Findlay, A. (2007) An approach to treating and managing severe physical disability. In: J. Rennie (ed.) Learning Disability: Physical therapy, treatment and management – a collaborative approach (2nd edn). Chichester: John Wiley.
Goldsmith, J. and Goldsmith, L. (2007) Postural care. In: J. Rennie (ed.) Learning Disability: Physical therapy, treatment and management – a collaborative approach (2nd edn.). Chichester: John Wiley.
